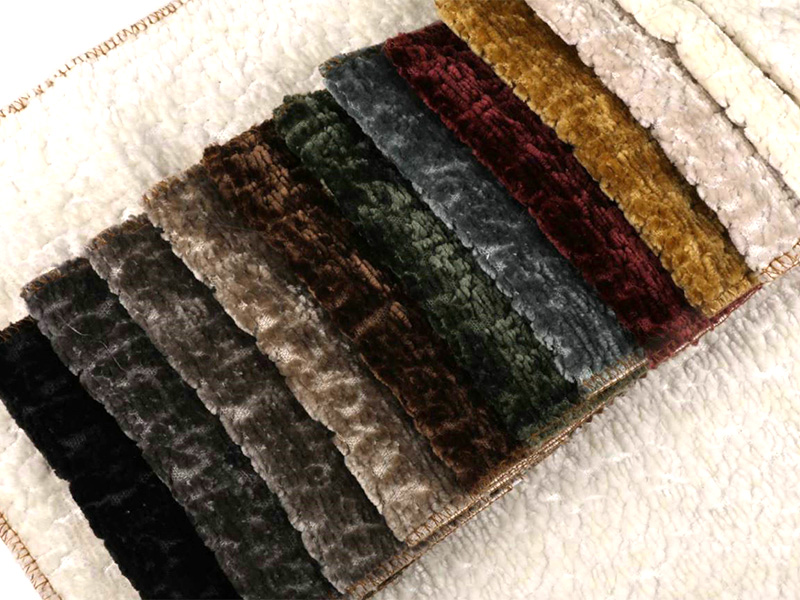
In the vibrant world of textile manufacturing, woven fabric factories stand as the cornerstone of innovation and precision. These factories are where the magic of transforming raw materials into exquisite fabrics takes place, catering to a wide range of industries from fashion to home furnishings, automotive to industrial applications. A woven fabric factory is not just a place of production; it is a hub of creativity, technology, and sustainability.
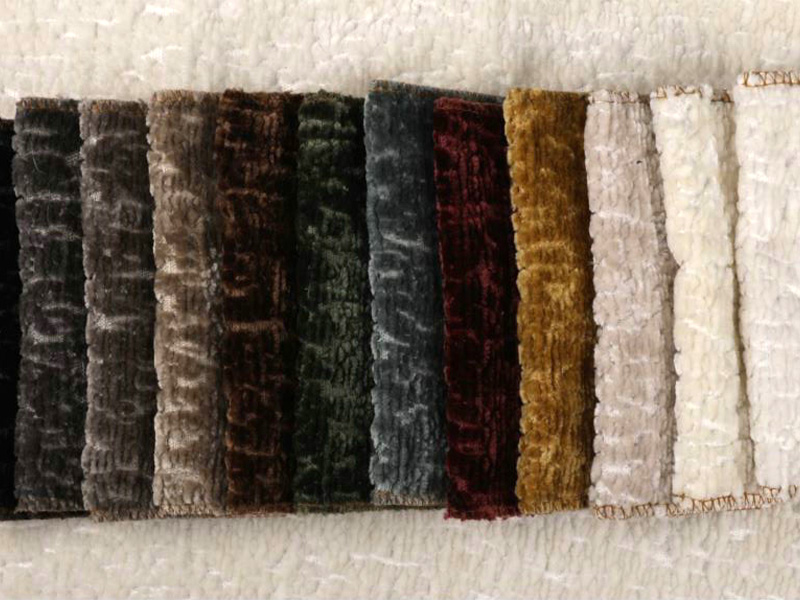
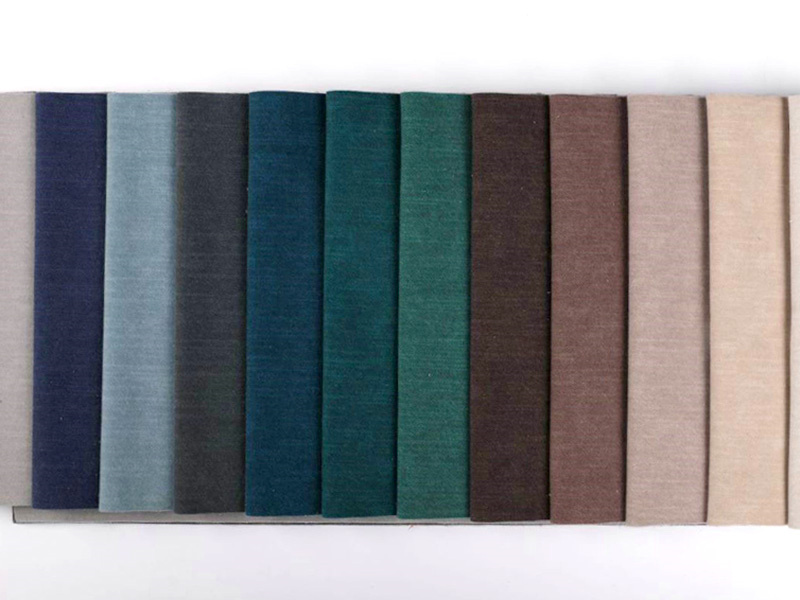
At the heart of every woven fabric factory lies the art of weaving. Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two sets of yarns—the warp (lengthwise) and the weft (crosswise)—at right angles to each other. This process forms the basis of various fabric structures, including plain weave, twill, and satin, each offering unique properties in terms of strength, texture, and appearance.
The weaving process itself is a testament to human ingenuity and mechanical precision. Modern looms, ranging from simple shuttle looms to highly advanced air-jet and rapier looms, enable factories to produce fabrics with exceptional quality and efficiency. These machines are operated by skilled technicians who possess a deep understanding of yarn tension, fabric construction, and the nuances of different fiber types.
The journey of a woven fabric begins with the careful selection of raw materials. Factories source a variety of fibers, including natural fibers like cotton, wool, and silk, as well as synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic. The choice of fiber depends on the end-use of the fabric, customer preferences, and cost considerations.
For instance, cotton is prized for its breathability and softness, making it ideal for apparel and home textiles. Wool, on the other hand, offers excellent insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making it suitable for outerwear and high-end suiting. Synthetic fibers are valued for their durability, wrinkle resistance, and colorfastness, making them popular in performance wear and industrial applications.
Quality control is a critical aspect of woven fabric production. Factories employ rigorous testing procedures to ensure that fabrics meet the required standards in terms of strength, colorfastness, shrinkage, and other performance metrics. Advanced technologies such as spectrophotometers and tensile testing machines are used to measure fabric properties with precision.
Innovation is another key driver in the woven fabric industry. Factories are constantly exploring new fiber blends, finishes, and weaving techniques to enhance fabric performance and aesthetics. For example, the use of nanotechnology in fabric finishes can impart antimicrobial, water-repellent, or UV-protective properties to fabrics. Similarly, the development of smart textiles that can monitor health indicators or change color based on environmental conditions is pushing the boundaries of what woven fabrics can do.
In recent years, sustainability has become a major focus for woven fabric factories. With growing consumer awareness and regulatory pressures, factories are adopting eco-friendly practices to minimize their environmental footprint. This includes using recycled fibers, reducing water and energy consumption, and implementing waste management systems.
For instance, many factories are now using recycled polyester made from post-consumer plastic bottles to produce fabrics. This not only reduces waste but also conserves natural resources. Additionally, the use of eco-friendly dyes and chemicals in the finishing process helps to minimize pollution and protect worker health.

 English
English русский
русский